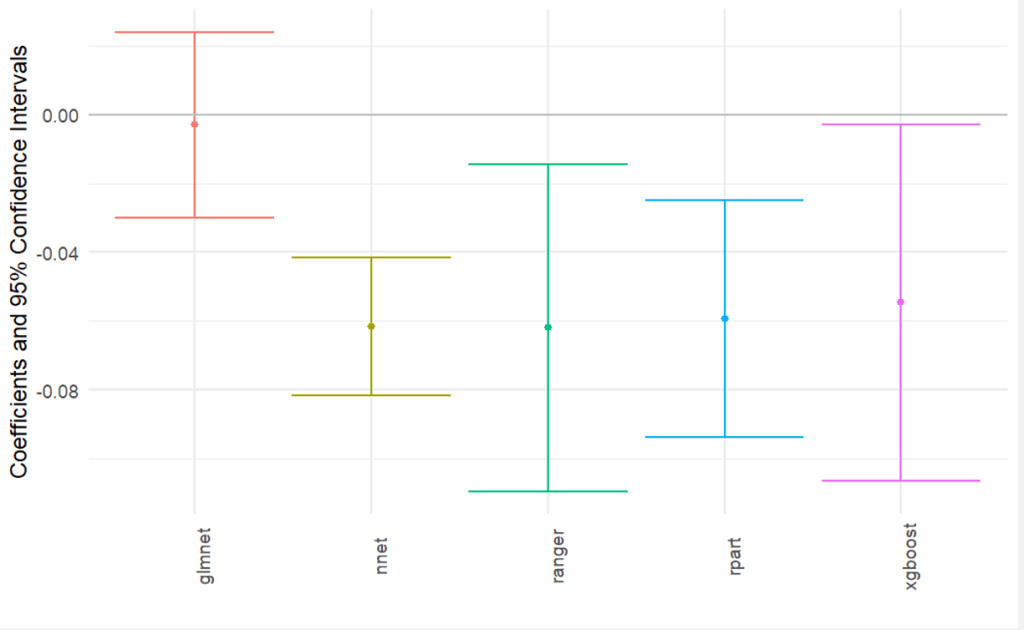- Group project
- I helped lead the design and completion and performed substantive troubleshooting on all aspects.
- Goal: Isolate the effect (linear coefficient) of remote work’s effect on PM2.5 air pollution in U.S. metropolitan areas
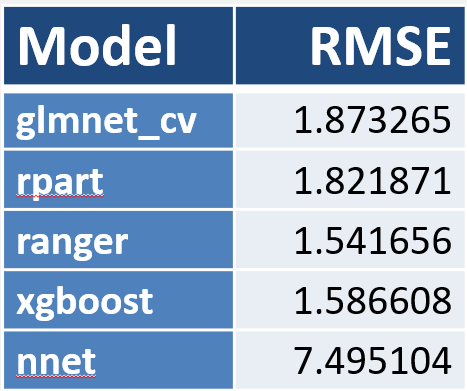
- Method: Compared multiple approaches to weight the covariates in a Double ML model
- Ultimately selected random forest (aka ranger)
- Result: a 50 percent increase in remote work could reduce the amount of PM2.5 in the air by about 25 percent of the EPA standard.
- Data from EPA and Census Bureau
- Coded in R
- tidycensus
- mlr3
- DoubleML
- Github for version control